下記のBB本の続きだが、
カラー図解 Raspberry Piではじめる機械学習 基礎からディープラーニングまで
Google Colaboratory環境は、Piとほぼ同じとわかったので、これからの実験はGoogle Colaboratoryで行う。
線形サポートベクトルマシンのコードがよくわからないので、そのままコピペ
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from sklearn import datasets, svm
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
# アヤメのデータをロードし、変数irisに格納
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# 特徴量のセットを変数Xに、ターゲットを変数yに格納
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# 特徴量を外花被片の長さ(sepal length)と幅(sepal width)の
# 2つのみに制限(2次元で考えるため)
X = X[:,:2]
# ターゲットは2 (iris virginica) でないもの,
# つまり iris setosa (0) と iris versicolor (1) のみを対象とする
# (領域の2分割)
X = X[y!=2]
y = y[y!=2]
# 分類用にサポートベクトルマシン (Support Vector Classifier) を用意
clf = svm.SVC(C=1.0, kernel='linear')
# データに最適化
clf.fit(X, y)
##### 分類結果を背景の色分けにより表示
# 外花被片の長さ(sepal length)と幅(sepal width)の
# 最小値と最大値からそれぞれ1ずつ広げた領域を
# グラフ表示エリアとする
x_min = min(X[:,0]) - 1
x_max = max(X[:,0]) + 1
y_min = min(X[:,1]) - 1
y_max = max(X[:,1]) + 1
# グラフ表示エリアを縦横500ずつのグリッドに区切る
# (分類クラスに応じて背景に色を塗るため)
XX, YY = np.mgrid[x_min:x_max:500j, y_min:y_max:500j]
# グリッドの点をscikit-learn用の入力に並べなおす
Xg = np.c_[XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()]
# 各グリッドの点が属するクラス(0か1)の予測をZに格納
Z = clf.predict(Xg)
# Zをグリッド上に並べなおす
Z = Z.reshape(XX.shape)
# クラス0 (iris setosa) が薄オレンジ (1, 0.93, 0.5, 1)
# クラス1 (iris versicolor) が薄青 (0.5, 1, 1, 1)
cmap01 = ListedColormap([(0.5, 1, 1, 1), (1, 0.93, 0.5, 1)])
# 背景の色を表示
plt.pcolormesh(XX, YY, Z==0, cmap=cmap01)
# 軸ラベルを設定
plt.xlabel('sepal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
##### ターゲットに応じた色付きでデータ点を表示
# iris setosa (y=0) のデータのみを取り出す
Xc0 = X[y==0]
# iris versicolor (y=1) のデータのみを取り出す
Xc1 = X[y==1]
# iris setosa のデータXc0をプロット
plt.scatter(Xc0[:,0], Xc0[:,1], c='#E69F00', linewidths=0.5, edgecolors='black')
# iris versicolor のデータXc1をプロット
plt.scatter(Xc1[:,0], Xc1[:,1], c='#56B4E9', linewidths=0.5, edgecolors='black')
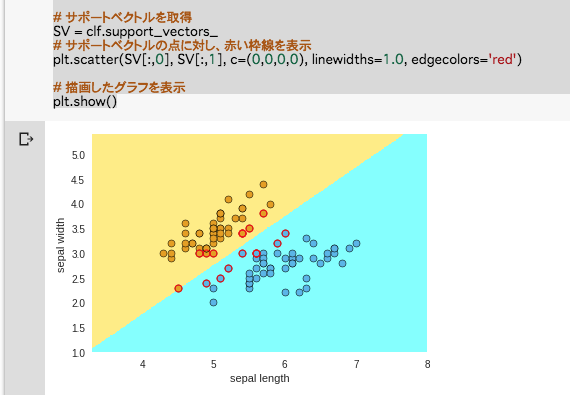
# サポートベクトルを取得
SV = clf.support_vectors_
# サポートベクトルの点に対し、赤い枠線を表示
plt.scatter(SV[:,0], SV[:,1], c=(0,0,0,0), linewidths=1.0, edgecolors='red')
# 描画したグラフを表示
plt.show()
結果の出力